What is Enterprise Risk Management? In an Era Where Uncertainty Is Unavoidable, risk has become an issue that every organization must face in various forms whether it is natural disasters, economic problems, data breaches, or even political changes. These can lead to financial, operational, legal, and reputational risks. Without proper enterprise risk management, such risks can severely impact business operations and goals. This is why Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) has become an essential tool for modern businesses.
This article will guide you through a deep understanding of what ERM is, why it matters, and what components and strategies can help your business grow with stability and sustainability even in the face of uncertainty.
What Is Risk ?
Risk refers to the possibility of an undesirable event occurring in the future that could impact an organization’s objectives either positively or negatively. Risk Management is the process of identifying, assessing, planning responses to, and monitoring risks to ensure that the organization can achieve its goals effectively. It aims to reduce the likelihood and impact of negative outcomes while enhancing the organization’s ability to respond during crises. The focus is on creating a balance between the expected return and the acceptable level of risk.
What Is ERM or Enterprise Risk Management?
ERM, short for Enterprise Risk Management, is an integrated and systematic approach to managing risks across an organization. Unlike traditional risk management, which often views risks in isolated aspects within individual departments, ERM takes a holistic view of the entire organization. It considers risks across all dimensions, from strategic and financial risks to operational, legal, and reputational risks.
ERM is not just about preventing damage; it is a process that incorporates risk into business decision-making. This enables organizations to identify, assess, manage, and monitor risks effectively, allowing them to respond to unexpected situations and even uncover new opportunities that add long-term value to the business.
What Are the Characteristics of Enterprise Risk Management?
Enterprise Risk Management is a risk management approach that stands out from traditional methods in several key ways:
-
Ongoing Process:
ERM is not a one-time activity. It is a continuous process that evolves with changes in the organization and the business environment. -
Enterprise-wide)
ERM considers risks across all departments and levels of the organization, from top executives to operational staff, while recognizing the interconnections between different types of risks. -
Strategic Alignment:
Risk management must support the organization’s goals and strategies. ERM is integrated into strategic planning and business decision-making, making risk consideration a core part of driving the organization forward. -
Driven by Board and Management:
The success of ERM depends on the commitment and support of the board of directors and senior management, who play a key role in setting policies and direction. -
Value-Focused:
ERM aims not only to protect the organization’s value but also to create new opportunities through effective risk management. It uses clear risk indicators to help increase long-term value.
What Are the Components of Enterprise Risk Management?
The key components of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM), based on international standards such as ISO 31000 and the widely adopted COSO ERM 2017 framework, consist of interconnected elements that work together as follows:
-
Governance and Culture)
Establishing an organizational atmosphere and culture that prioritizes risk management, with clearly defined roles, responsibilities, and governance frameworks led by senior management. -
Strategy and Objective-Setting)
Integrating risk management into the organization’s strategy and objective-setting to ensure that acceptable risk levels align with the organization’s goals. -
Performance:
Core processes for identifying, assessing, managing, and prioritizing risks at all levels of the organization. -
Review and Revision:
Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of risk management to ensure ERM remains relevant and effective amid changing conditions. -
Information, Communication and Reporting:
Creating a clear and timely risk communication system for stakeholders at all levels, including the use of appropriate technologies and tools for data analysis.
Why Is Enterprise Risk Management Important for Businesses?
Enterprise Risk Management is a core element in building organizational stability and sustainability. It enables businesses to anticipate and respond to risks systematically, providing a long-term competitive advantage. Implementing ERM in an organization is highly important and offers benefits in several areas:
-
Protecting and Enhancing Organizational Value:
ERM helps organizations proactively identify and manage risks that could lead to loss of assets, revenue, or reputation, while also uncovering hidden opportunities. -
Supporting Better Decision-Making:
When executives have completed and structured risk information, business decisions become more thoughtful and less prone to error. -
Increasing Stakeholder Confidence:
Effective enterprise risk management builds trust among investors, partners, customers, and regulators, enhancing the organization’s credibility and stability. -
Improving Operational Efficiency:
Risk assessments help identify weaknesses in workflows and improve operational performance. -
Creating Competitive Advantage:
Organizations with strong risk management are more agile and responsive to market changes, allowing them to seize opportunities and grow continuously.
What Makes Good Enterprise Risk Management?
Effective Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) must be comprehensive across all levels, flexible, data-driven, clearly led, and naturally integrated into the organizational culture. A successful ERM system should have the following characteristics:
-
Aligned with Strategy:
ERM should not be just a trend-driven activity, it must be a tool that genuinely supports and drives the organization’s strategies and goals. -
Comprehensive)
It must be able to identify and assess all types of risks, including both measurable and hard-to-quantify risks. -
Systematic and Dynamic:
ERM should have a clear framework and processes, with regular reviews and updates to stay aligned with changing environments. -
Effective Communication:
Risk information and management approaches must be communicated openly and promptly across all levels of the organization. -
Measurable:
There should be clearly defined Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) to monitor and evaluate risks in a tangible way.
What Makes Enterprise Risk Management Successful?
Achieving success in Enterprise Risk Management is not solely dependent on tools or software. There are several other critical factors, including:
-
Top Management Commitment:
Top managements must genuinely demonstrate the importance of ERM by setting policies, allocating budgets, and serving as role models in fostering a risk-aware culture within the organization. -
Communication and Awareness:
Regular communication is essential to ensure that employees at all levels understand the importance of ERM and their roles in managing organizational risks. -
Integration into Operations:
ERM must be embedded into employees’ daily activities—not just something done at year-end. It should also be integrated with the Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) to support organizational sustainability. -
Appropriate Technology:
Using ERM software or platforms is a helpful option for efficiently collecting, analyzing, and reporting risk data.
What Are the Common Global Strategies for Enterprise Risk Management?

In managing organizational risks, businesses can choose appropriate strategies based on the severity of each risk. The commonly used global strategies include:
-
Risk Acceptance:
Choosing to accept certain risks because the likelihood of occurrence is low, the impact is minimal, or the cost of managing the risk outweighs the potential benefit. -
Risk Avoidance:
Deciding not to engage in activities or projects that may lead to certain risk, for example, avoiding investment in high-risk or highly volatile businesses. -
Risk Reduction/Mitigation:
Taking actions to reduce the likelihood of a risk occurring or to lessen its impact if it does occur, such as installing safety systems or providing employee training. -
Risk Transfer:
Shifting the risk to another party, for example, purchasing insurance to transfer financial risk to an insurance company.
What Are the Steps in Enterprise Risk Management?
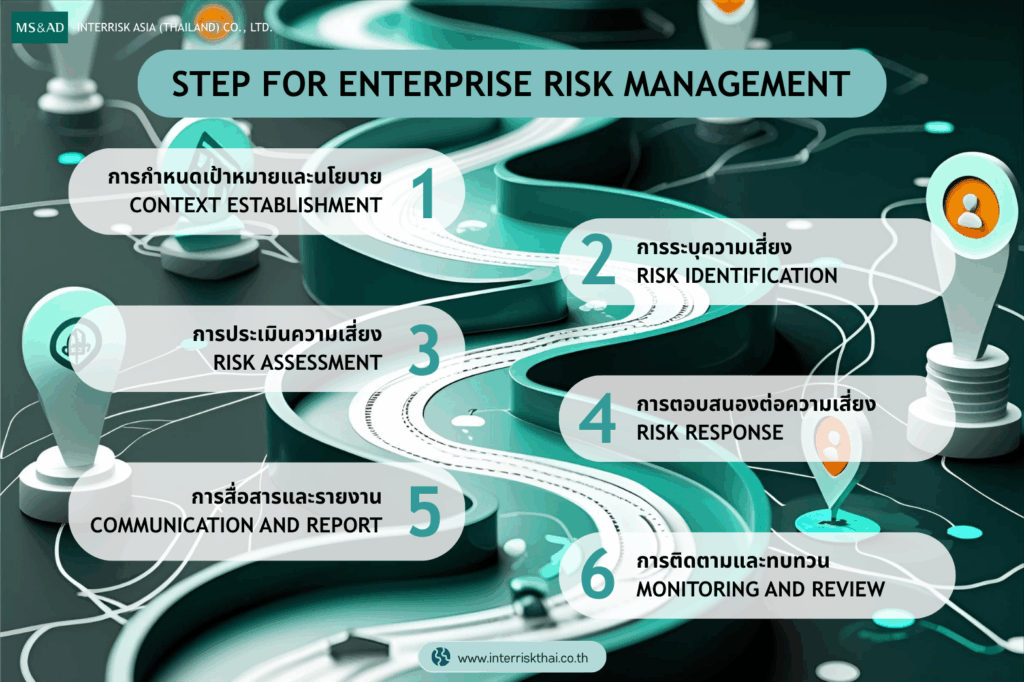
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) requires a comprehensive view of various types of risks within an organization, such as strategic, financial, operational, legal, and reputational risks. Implementing ERM in an organization can be done through the following steps:
-
Context Establishment:
Define the objectives of ERM, the acceptable level of risk for the organization, and related policies. -
Risk Identification:
Identify and gather information on potential risks from all sources—both internal and external, that may impact the organization. -
Risk Assessment:
Analyze identified risks in terms of their likelihood of occurrence and impact to prioritize them. -
Risk Response:
Choose appropriate strategies (Accept, Avoid, Reduce, Transfer) to respond to each type of risk. -
Communication and Report)
Communicate and report risk information to relevant stakeholders to ensure understanding and effective response. -
Monitoring and Review:
Continuously monitor the progress of risk management and adjust plans as situations change.
Implementing Enterprise Risk Management with InterRisk Asia
In today’s world, where businesses face risks from all directions, enterprise risk management requires a detailed and systematic approach at every stage, from identifying risks to continuous monitoring. Using the right methodology is key to ensuring the ERM process is as effective as possible. If you are looking for a structured and efficient approach to enterprise risk management, contact our expert consultants at InterRisk Asia today, and rest assured that “your organization remains operational, even in times of crisis”.
InterRisk Asia is a leading business continuity consulting firm in Thailand, operates under the MS&AD Group from Japan.
End-to-end consulting for the development of a robust BCMS, with pathways to ISO 22301 certification
Specialized training programs designed for both management and staff to enhance awareness and competency in BCMS practices.
Analysis of operational risks and disruption impacts to inform the development of targeted continuity strategies.
Structured exercises to validate your BCP and strengthen organizational preparedness and response capabilities.
Experienced consultants with hands-on BCMS expertise
Customized planning tailored to your business context.
Practical tools and templates, with expert support for testing and improvement.

