Risk management is at the heart of preparing for uncertainties that could impact an organization’s goals or daily operations. Understanding the types of risks and their contributing factors allows for effective risk planning and management. Risk management involves establishing a system for assessing and analyzing potential risks before developing emergency plans and implementing systematic control measures, along with determining risk levels. This enables informed decision-making and mitigating potential future impacts.
Why risk management matters ?
Risk Management is the process by which an organization manages and controls its exposure to risk. Risk is the impact of uncertainty that may result in positive (opportunity), negative (threat), or both. We can assess riskbefore applying the information to risk management. Generally, risk is considered to be:
An effective risk management framework empowers organizations to proactively manage diverse categories of risk—ranging from workplace-related risks to those stemming from strategic, operational, financial, and legal factors. By evaluating risks across five defined levels, organizations can develop suitable mitigation and response strategies.
Framework of risk management
The risk management framework provides a structured foundation for embedding risk management into an organization’s core activities. Its effectiveness is highly dependent on the commitment and support of top management.
The development of a risk management framework aligned with ISO 31000 encompasses design, implementation, evaluation, and continuous improvement. The framework includes key components such as:
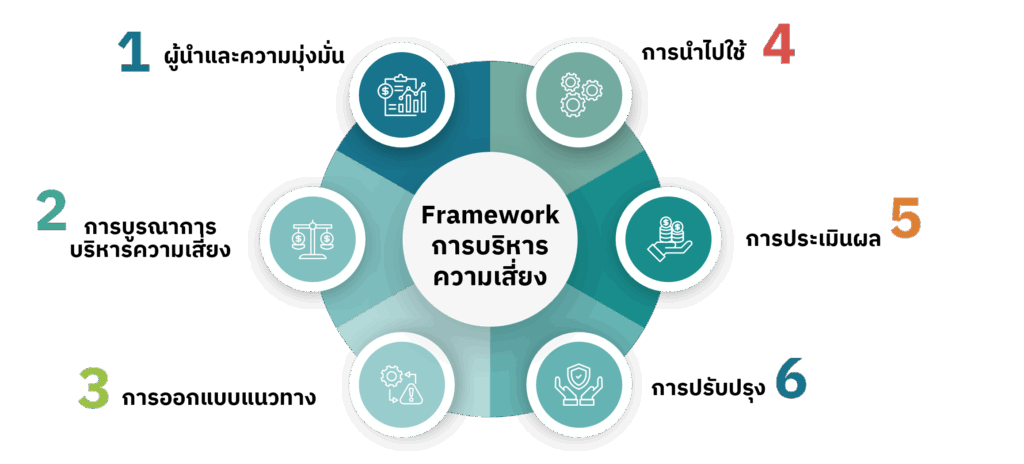
Leadership and commitment
Executives play a key role in risk management by demonstrating accountability and actively supporting risk-related initiatives at all levels of the organization.
Integration
Risk management must align with the organization's structure and context, where everyone has a role to play in managing risk.
Designing
The risk management framework requires a clear understanding of both the internal and external context of the organization. It involves defining roles and responsibilities, allocating appropriate resources, and establishing an effective communication system.
Implementation
Building active participation and risk awareness throughout the organization is crucial for managing uncertainty in a clear and structured manner.
Evaluation
The performance of the framework should be regularly measured to ensure it continues to meet the organization’s objectives.
Improvement
The framework must be continuously developed and improved based on identified gaps and opportunities for enhancement.
How many of risk management ways
Risk management is a process that organizations use to identify, assess, and manage risks that may impact their objectives or operations. In general, there are several methods for managing risk, which can be categorized into the following main approaches:
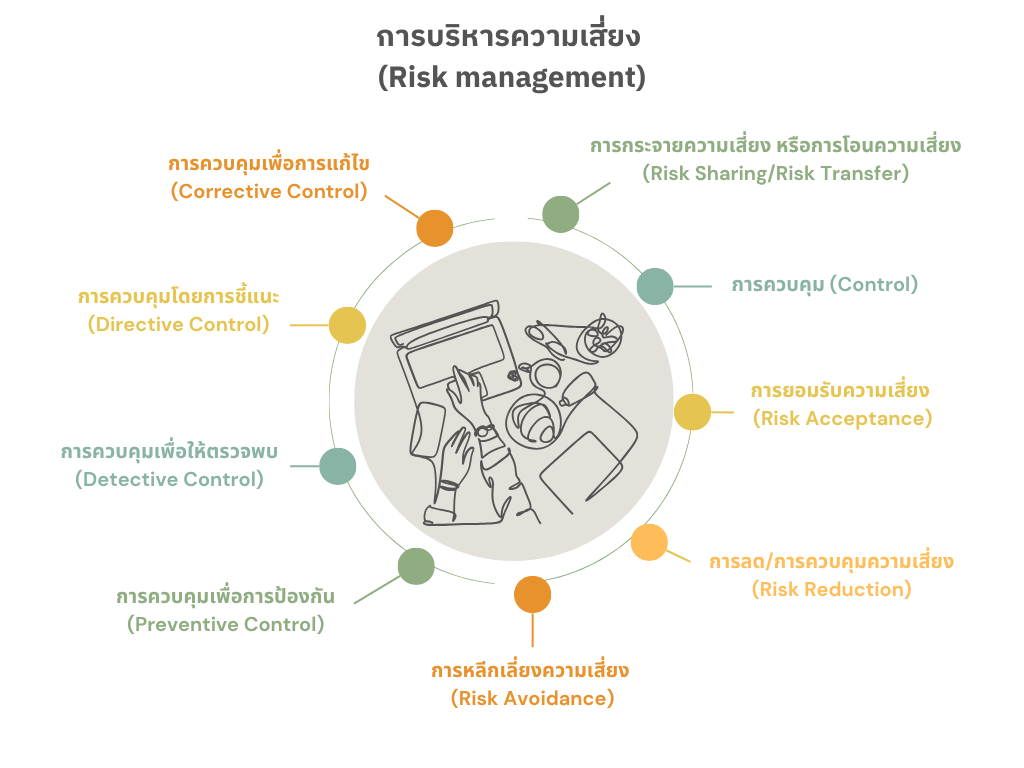
Risk Sharing or Risk Transfer
aims to reduce the impact of operational risks by sharing or transferring them to other individuals or organizations. Examples include purchasing insurance, outsourcing to external contractors, or entering into joint ventures with strategic partners.
Risk Control
involves applying appropriate strategies to manage risks within acceptable thresholds, including policy development, the use of technological solutions, and staff training programs.
Risk Acceptance
refers to the decision to take no specific action toward a risk, acknowledging and accepting its potential impact—especially when the risk is considered low in probability or severity.
Risk Reduction
involves taking actions to reduce the likelihood or impact of risks, such as improving work processes, enhancing control systems, or implementing technology-based preventive measures.
Risk Avoidance
involves avoiding activities or situations that may lead to risk, such as choosing not to invest in high-risk ventures or canceling projects with uncertain outcomes.
Risk Preventive Control
involves taking preemptive actions to eliminate or minimize the possibility of risks arising. Common practices include implementing security systems, conducting staff training, and setting clear operational standards.
Risk Detective Control
involves taking preemptive actions to eliminate or minimize the possibility of risks arising. Common practices include implementing security systems, conducting staff training, and setting clear operational standards.
Risk Directive Control
emphasizes influencing behavior through structured guidance, including the development of work manuals, policy formulation, and clear communication of standard operating procedures.
Risk Corrective Control
are taken to address and restore operations following a risk incident. These may include recovering lost data, upgrading systems, or modifying workflows to prevent recurrence.
Benefit of Risk management
Risk Management offers significant benefits at both organizational and personal levels, especially in an era where uncertainty can arise at any moment. Organizations can identify and manage risks before problems occur, reducing the likelihood of financial loss, reputational damage, and resource depletion. Risk assessment provides executives with comprehensive information for decision-making, considering both opportunities and threats. Effective risk management enables organizations to operate continuously, even in unexpected situations, and builds confidence among stakeholders—whether customers, investors, or employees. Having a clear risk management system fosters trust and enhances the organization’s image.
Free Download! Example of Risk Management in PDF file with Techniques
A sample Risk Management PDF prepared by InterRisk Asia covers key topics such as:
Risk identification, Factors contributing to Risks, Five levels of Risk Severity, Risks in workplace, and Example of Risk Assessment and Management.
Risk management with INTERRISK ASIA
In summary, a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) is a business continuity framework that enables organizations to effectively respond to unexpected events through systematic risk analysis, management, and proactive planning. Organizations with a BCMS in place can maintain continuous operations, build trust with customers and stakeholders, and minimize potential impacts.
InterRisk Asia (Thailand) is a company specializing in Business Continuity Management (BCM) services. We provide comprehensive support ranging from Business Impact Analysis, Risk Assessment, Business Continuity Plan to training, drills, and consulting services in accordance with ISO 22301 standard.ur goal is to help organizations effectively and sustainable prepare for and respond to incidents of all scales.
End-to-end consulting for the development of a robust BCMS, with pathways to ISO 22301 certification
Specialized training programs designed for both management and staff to enhance awareness and competency in BCMS practices.
Analysis of operational risks and disruption impacts to inform the development of targeted continuity strategies.
Structured exercises to validate your BCP and strengthen organizational preparedness and response capabilities.
Experienced consultants with hands-on BCMS expertise
Customized planning tailored to your business context.
Practical tools and templates, with expert support for testing and improvement.

