Risk management in an organization does not only mean preventing incidents from happening, but also preparing to respond and recover when they actually occur. Without a clear response plan, the impact can be severe—operations may come to a halt, revenue may be lost, and customer trust may be damaged. Having an emergency response plan is therefore not just a ‘nice-to-have,’ but a ‘must-have’ to protect both people and the business from crises.
HIGHLIGHTS:
A contingency Plan is a backup plan prepared in advance to deal with events that may occur and disrupt business operations.
An emergency Plan is an immediate response plan activated when an emergency occurs, focusing primarily on protecting lives and property.
A business Continuity Plan (BCP) is a master plan that covers prevention, response, and recovery, ensuring that the business can continue operating even in the face of major crises.
Each type of plan serves a different purpose, so the planning process should begin with defining objectives, analyzing and assessing risks, prioritizing actions, and regularly testing the plan to ensure it achieves its intended goals and objectives.
What is a Contingency Plan?

A Contingency Plan is an operational backup plan developed by an organization to address potential events that could impact operations. It is not limited to emergencies related to safety, but also covers business issues such as IT system failures, supply chain disruptions, or the loss of critical resources. The key strength of this plan lies in preparing ‘alternative options’ in advance, so that the business can continue operating even in the face of disruptions.
Main Objectives of a Contingency Plan
- Reduce the impact on operations when unexpected events occur
- Build confidence among customers and stakeholders that the organization is prepared
- Maintain operations and minimize revenue loss
- Enable faster and more well‑directed decision‑making during crises
Examples of Use in Organizations
IT: Develop backup plans for servers and cloud systems in case the primary system fails, ensuring uninterrupted customer service.
Manufacturing: Prepare alternative suppliers in advance in case the main supplier cannot deliver raw materials on schedule.
Financial Institutions: Establish backup operations from other branches if the main branch cannot open due to unforeseen events.
What is an Emergency Plan?

An Emergency Plan is an immediate response plan activated when an emergency occurs that affects the safety of personnel and organizational asset. For examples, fire emergency plans flood emergency plans earthquake emergency plans, or serious accident response plans. The key point of this plan is to have clear procedures that can be implemented immediately to prevent loss and minimize damage.
Main Objectives of an Emergency Plan
- Protect the lives and safety of employees, customers, and stakeholders
- Reduce damage to the organization’s assets and infrastructure
- Establish systematic procedures for evacuation, alerts, and coordination
- Ensure confidence that the organization is prepared to handle emergencies
Examples of Situations Requiring an Emergency Plan
Fire in an office building: Procedures for evacuating employees to a safe assembly point, supported by alarm systems and an internal firefighting team.
Flash flood: Plans for relocating critical equipment and shutting down electrical systems to prevent hazards.
Earthquake: Guidelines such as taking cover under desks, evacuating the building, and conducting safety checks after the incident.
Serious accident in a factory: Availability of a first aid team and immediate procedures for notifying relevant authorities.
What is a Business Continuity Plan (BCP)?

A Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is a strategic plan developed by an organization to ensure that business operations can continue even in the event of unexpected incidents or crises that affect work, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or disruptions to critical systems. This plan encompasses prevention, response, and recovery, enabling the business to return to normal operations as quickly as possible.
Main Objectives of a Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
- Maintain business continuity: Minimize disruptions that could lead to revenue loss and customer attrition.
- Build confidence: Ensure customers and stakeholders trust that the organization is prepared to handle crises.
- Reduce financial impact: Having a clear plan helps lower costs associated with disruptions and recovery.
- Comply with standards and regulations: Many industries, such as finance and insurance, require organizations to have a BCP as a mandatory practice.
Practical Examples of BCP Implementation
Bank: Maintain backup IT systems and data centers to ensure continuous customer service even if the primary system fails.
Hospital: Develop continuity plans to keep patient services running during power outages or disasters.
Logistics company: Establish alternative transportation routes and multiple partners to prevent supply chain disruptions.
Operations: Implement remote work plans so employees can continue working during pandemics or events that prevent access to the office.
The Differences Between Contingency Plan, Emergency Plan, and BCP
We often confuse Contingency Plan, Emergency Plan และ Business Continuity Plan (BCP), since all three are designed to address unexpected events. In reality, however, each plan has distinct objectives, scope, and roles. Understanding these differences helps organizations select and integrate the right plans appropriately, ensuring resilience both in the short term and the long term.
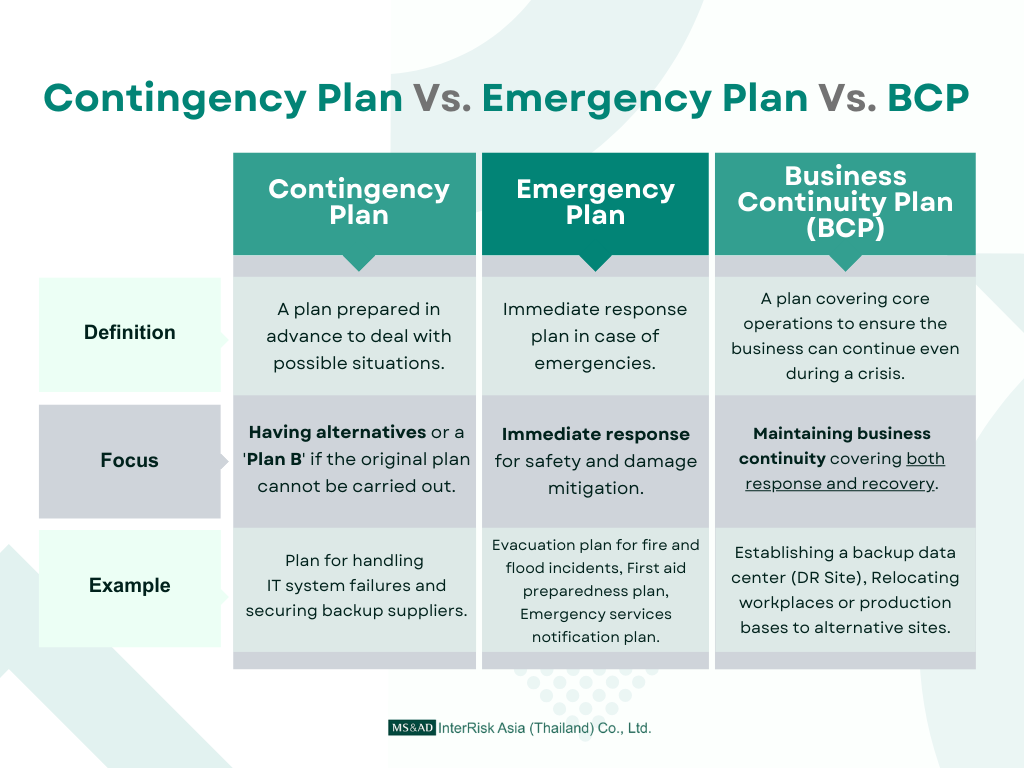
Key Differences
- Contingency Plan focuses on preparing specific backup options so that the business can continue operating even when disruptions occur. - Emergency Plan focuses on immediate response to protect lives and property when emergencies happen. - BCP (Business Continuity Plan) เfocuses on maintaining overall business continuity, covering prevention, response, and recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How is an Emergency Plan different from a BCP (Business Continuity Plan)?
An Emergency Plan is designed for immediate response when emergencies occur, such as fires, floods, or serious accidents. In contrast, a BCP has a broader scope, covering prevention, response, and recovery, to ensure that the business can continue operating during a crisis—not just managing the immediate emergency.
How is a Contingency Plan different from an Emergency Plan?
A Contingency Plan is a backup plan prepared in advance to deal with potential events, while an Emergency Plan is an immediate response plan activated when an actual emergency occurs, focusing on protecting lives and property.
If an organization already has an Emergency Plan, is it still necessary to have a BCP?
It is necessary, because an Emergency Plan focuses on immediate response, while the primary goal of a BCP is to maintain business continuity—not just to handle emergencies in the moment—and to ensure the business can resume operations in a systematic and sustainable way. The two plans therefore complement each other and enable the organization to be prepared for all dimensions of risk.
How to Start Developing These Plans?
Start by defining objectives, analyzing risks, prioritizing resources, assigning team roles, and regularly testing the plan to ensure it can be effectively implemented when an incident occurs.
Ready to handle any situation may affect business continuity with InterRisk Asia
InterRisk Asia is a company in developing contingency plans and conducting business impact analysis. Services cover cause analysis, solution design, and preventive strategies. The company also provides training and consulting across multiple industries to help organizations prepare, minimize impacts, and restore business operations with confidence.
End-to-end consulting for the development of a robust BCMS, with pathways to ISO 22301 certification
Specialized training programs designed for both management and staff to enhance awareness and competency in BCMS practices.
Analysis of operational risks and disruption impacts to inform the development of targeted continuity strategies.
Structured exercises to validate your BCP and strengthen organizational preparedness and response capabilities.
Experienced consultants with hands-on BCMS expertise
Customized planning tailored to your business context.
Practical tools and templates, with expert support for testing and improvement.

